Efficacy has been defined in receptor pharmacology as a proportionality factor denoting the amount of physiological response a given drug imparts to a biological system. Design of drugs with predetermined efficacy is as significant as the design of receptor-selective drugs. Since the term efficacy of a drug is associated with the degree of activation of its receptor by this drug, understanding the receptor activation-associated structural changes would uncover the molecular mechanism that underlies efficacy, thus providing further information for the design of drugs with predetermined efficacy. To determine activation-associated structural changes of GPCRs, our laboratory, in collaboration with Jonathan Javitch (Columbia University, USA), perform a variety of experiments, using as prototype the beta2-adrenergic receptor (b2AR).
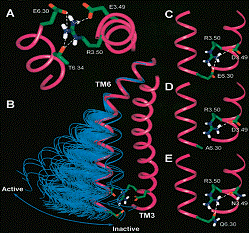
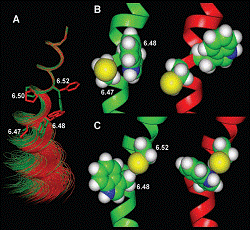
We found, in collaboration with Dr. Javitch that coordinated rotamer changes of residues 6.47, 6.48, and 6.52 in the sixth membrane-spanning domain (TM6) of beta2-adrenergic receptor appear to be associated with receptor activation. This rotamer toggle switch may impact the alpha-helix backbone and during receptor activation may modulate the movement of the TM6 about the Pro-kink (Fig.1). Such a receptor activation-associated conformational alteration may be associated with the disruption of an ionic lock between the cytoplasmic ends of the third and sixth membrane-spanning domains of receptor, and their movement away from each other, as suggested by the results of our studies preformed in collaboration with Dr. Javitch, Dr. Juan Ballesteros and Dr. Ulrik Gether (Panum Institute, University of Copenhagen, Denmark) (Fig.2).
We are now working to elucidate more activation-associated conformational changes of beta2-adrenergic receptor, including those in the cytoplasmic regions of receptor, which are responsible for the interaction of the activated receptor with G-proteins.
Fig. 1. A three-dimensional molecular representations of the rotamer toggle switch
Fig. 2. Molecular three-dimensional representations of the interaction of membrane-spanning domains 3 (TM3) and 6 (TM6) at their cytoplasmic ends.